In Intrinsic Clotting Mechanism Which of the Following Is Used
For a small break in a blood vessel the sequence of vascular spasm platelet plug formation and coagulation results in the break being sealed off. This pathway is slower than the extrinsic pathway but more important.

Coagulation Cascade What Is It Steps And More Osmosis
Wiggins RC Cochrane CC.

. Crossref Medline Google Scholar. As such the proteins required for such clotting to take place are part of the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. Coagulation cascade has two pathways known as intrinsic and extrinsic pathway.
Platelets normally start the clotting process when theyreexposed to the air such as in a cut or wound. Mechanism of Blood Clotting. The intrinsic pathway consists of factors I II IX X XI and XII.
The intrinsic pathway of coagulation and contact activation. Start studying the Blood Review Questions flashcards containing study terms like Which of the following are most active as phagocytes. Intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation.
The extrinsic clotting mechanism. Respectively each one is named fibrinogen prothrombin Christmas factor Stuart-Prower factor plasma thromboplastin and Hageman factor. Factor VII - stable factor or proconvertin.
The intrinsic pathway is activated by trauma inside the vascular system and is activated by platelets exposed endothelium chemicals or collagen. Once factor X has been activated by either the intrinsic or extrinsic pathway the enzyme prothrombinase converts factor II the inactive enzyme prothrombin into the active enzyme thrombin. B The intrinsic system occurs both in vivo and in vitro.
Both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways are involved in the formation of prothrombin activator and factor X. The following are coagulation factors and their common names. Intrinsic and extrinsic pathway are two types of pathways involved in the formation of blood clot.
Factor VI - unassigned. Basic laboratory tests used to identify blood clotting problems will also be presented. The extrinsic clotting mechanism.
Extrinsic Clotting Cascade Activated factor Xa is the site at which the intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation cascades converge. Formation of a blood clot called coagulation results from a series of reactions occurring in cascade. What are the 12 factors of blood clotting.
In this article we will discuss about the mechanisms and stages of blood clotting. Waterfall sequence for intrinsic blood clotting. This is followed by the sequential activation of factors xi and ix which results in the activation of factor x.
It involves factors XII XI IX VIII. Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam. Question 17 Thromboplastin release from tissues begins platelet plug formation.
The extrinsic pathway starts when there is a vascular tissue trauma or trauma. Blood loss is reduced and healing can begin. Activated factor X factor Xa initiates the common pathway of coagulation.
The intrinsic coagulation is induced by contact activation of FXII on negatively charged substrates followed by a downstream cascade of protein reactions resulting in the activation of prothrombin to thrombin Gorbet and Sefton 2004. Once a fibrin clot is formed and has performed its function of hemostasis mechanisms exist in the body to restore the normal blood flow by lysing the fibrin deposit. E rst referred to as the intrinsic or internal pathway occurs when a clot forms inside.
When blood comes into contact with negatively charged surfaces a series of proteolytic reactions are initiated that result in the activation of the plasma proteases factor FXII prekallikrein PK and FXI and the cleavage of high molecular weight kininogen HK. Coagulation also known as clotting is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel forming a blood clot. Blood clotting is initiated in one of two ways.
They stick together acting as a plug Platelets also activate the process which causes a fibrin. All the components necessary for the clotting process to proceed are found in the blood. C Intravascular thrombosis occurs by the extrinsic system.
Biliverdin and bilirubin are pigments that result from the breakdown of red blood cells. The mechanism by which coagulation allows for hemostasis is an intricate process that is done through a series of clotting factors. The intrinsic pathway starts when there is a trauma in blood or when blood is exposed to a collagen.
Crossref Medline Google Scholar. The result is a meshwork of a protein called fibrin. The extrinsic clotting mechanism.
Platelets aggregate to the site of the injury. 79 About the coagulation mechanism all the following is true except. When injury occurs vessel walls constrict causing reduced blood flow to the site of injury.
A Platelet factor 3 is required for both the extrinsic and intrinsic systems. An enzyme cascade in the blood clotting mechanism and its function as a biochemical amplifier. The basic event in the formation of a blood clot is the change of A.
The key difference between intrinsic and extrinsic pathways in blood clotting is their initiation factors. Factor II - prothrombin. Additionally what initiates the extrinsic clotting mechanism.
It is used clinically to dissolved clots in coronary arteries following a heart attack. Both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways belong to secondary hemostasis mechanisms. The intrinsic clotting mechanism.
This pathway involves a series of proteins protein cofactors and enzymes which interact in reactions that take place on membrane. Note that if the enzyme thrombin were not normally in an inactive form. The intrinsic clotting mechanism.
The mechanism of coagulation involves activation adhesion and aggregation of platelets as well as deposition and maturation of fibrin. It is also used to dissolved clots in the brain following stroke. Intrinsic pathway of coagulation a sequence of reactions leading to fibrin formation beginning with the contact activation of factor xii.
It potentially results in hemostasis the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel followed by repair. Following this the collagen fibres are exposed and the process View the full answer Transcribed image text. Both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways lead to the common pathway in which fibrin is produced to seal off the vessel.
Factor I - fibrinogen. Intrinsic system of coagulation Cells that facilitate blood clotting by forming a platelet plug and releasing chemicals into the coagulation cascade in the blood. Both intrinsic and extrinsic pathway end up in the common pathway.
The release of tissue thromboplastin initiates A. The intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation cascades are initiated by Factor XII FXII and tissue factor TF. The blood clotting process are vasoconstriction platelet activation thrombus formation and dissolution of the clot.
D The intrinsic system utilizes factors VIII IX XI and XII. A Basophils B Eosinophils C Erythrocytes D Neutrophils 2. Factor III - tissue thromboplastin tissue factor Factor IV - ionized calcium Ca Factor V - labile factor or proaccelerin.
The autoactivation of rabbit.
What Are The Similarities Between Intrinsic And Extrinsic Pathways Of Blood Coagulation Quora

Ch 14 Blood Flashcards Quizlet

The Classical Coagulation Model Two Pathways Intrinsic And Extrinsic Download Scientific Diagram

Hemostasis And Blood Coagulation Blood Cells Immunity And Blood Coagulation Guyton And Hall Textbook Of Medical Physiology 12th Ed

Intrinsic Coagulation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Bleeding And Blood Clotting Intrinsic Pathway Of Blood Coagulation Britannica
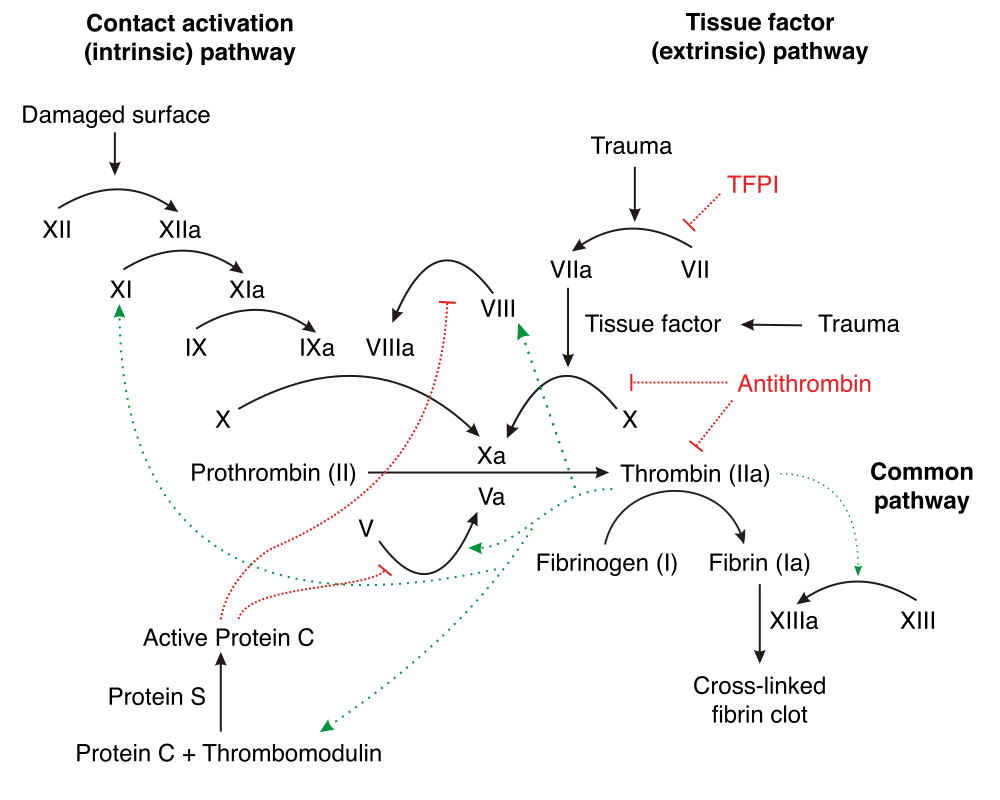
Coagulation Intrinsic Extrinsic Fibrinolysis Teachmephysiology
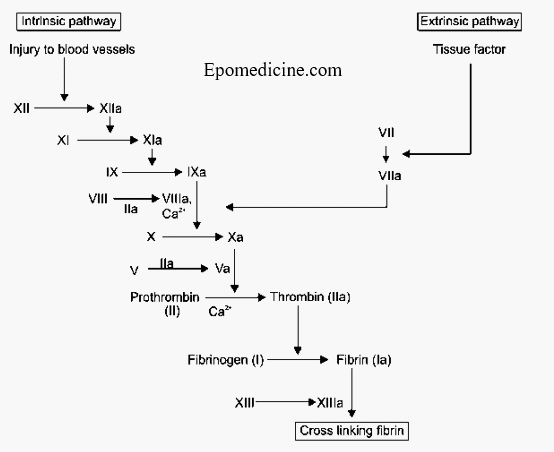
Simple Coagulation Cascade With Mnemonics Epomedicine

Intrinsic Pathway An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Overview Of Coagulation Cascade Diagram Of The Multistep Intrinsic Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic Representation Of The Coagulation Cascade And The Download Scientific Diagram
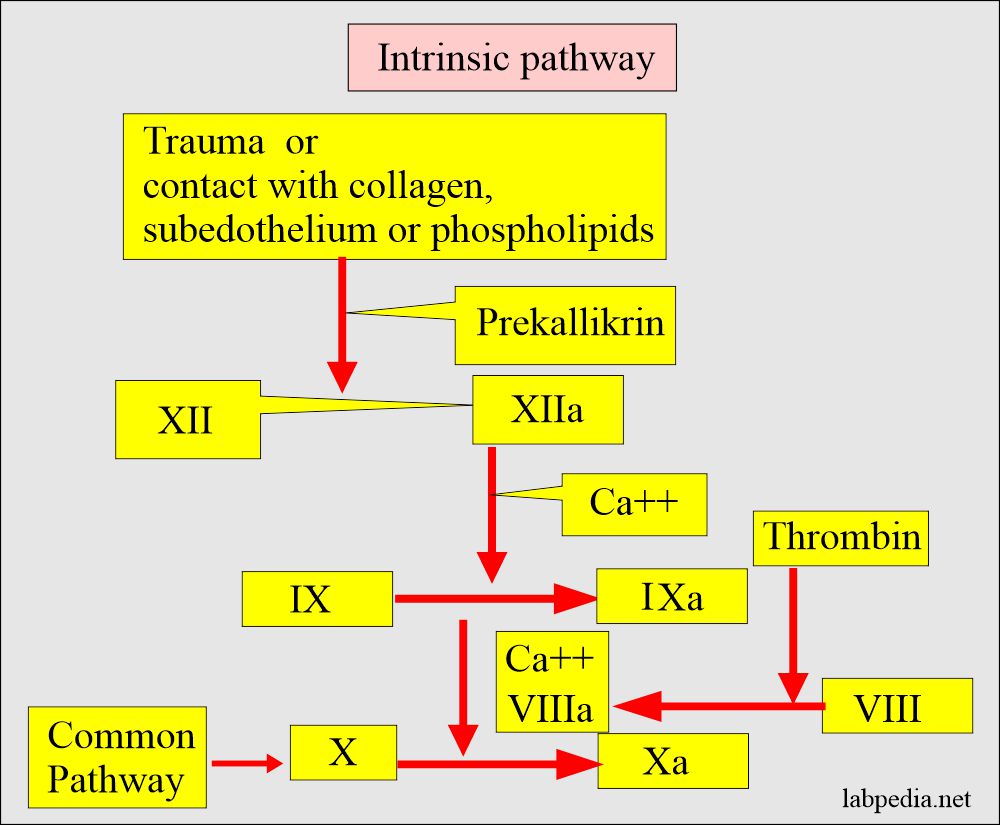
Coagulation Part 1 Blood Coagulation Process Coagulation Factors Assay And Factors Deficiency Labpedia Net

The Classical Coagulation Model Two Pathways Intrinsic And Extrinsic Download Scientific Diagram

The Intrinsic Extrinsic And Common Pathways Of The Coagulation Download Scientific Diagram
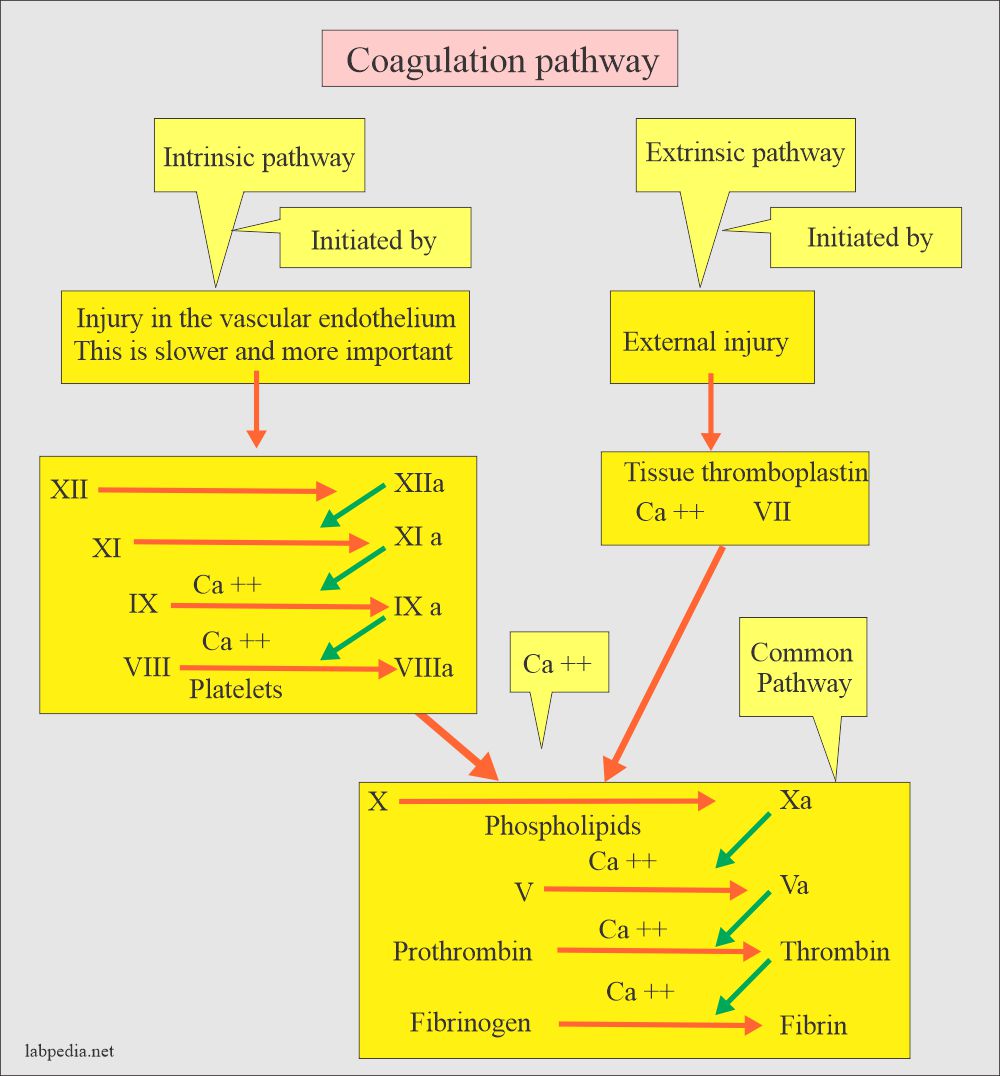
Blood Coagulation Factor And Interpretations

Hemostasis Anatomy And Physiology Ii

The Intrinsic Extrinsic And Common Pathways Of The Coagulation Download Scientific Diagram

Intrinsic Pathway An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Hemostasis And Blood Coagulation Blood Cells Immunity And Blood Coagulation Guyton And Hall Textbook Of Medical Physiology 12th Ed
Comments
Post a Comment